CAC Payback Period is a top operator and investor metric. It’s part of my Five Pillar SaaS Metrics Framework. It’s core to GTM efficiency calculations.
There are many flavors of CAC Payback Period now. I’ll cover the traditional metric that you must master in your SaaS business. However, you should consider the Dollar-based CAC Payback Period and CAC Payback Period+ when you have subscription and variable revenue.
Don’t forget to download the CAC Payback Period Excel template at the bottom of this post.
Updated for 2025.
CAC Payback Period Definition
CAC Payback Period is the number of months required to pay back the upfront customer acquisition costs after accounting for the variable expenses to service that customer. Simply put, CAC Payback Period equals CAC divided by the gross margin dollars generated by that customer.
CAC ties up working capital in our SaaS business. The longer our payback period, the longer we have to wait for that cash to come back to us. If we try to push high growth with long payback periods, your business will require more and more capital to grow on a unit basis.
CAC Payback Period Formula
We need thee inputs for our formula. CAC, Cohort ARR, and our subscription gross margin percentage. Since I am using ARR in the formula, we must multiply by 12 to put it in months. If you are using MRR, drop the “*12” from the formula.
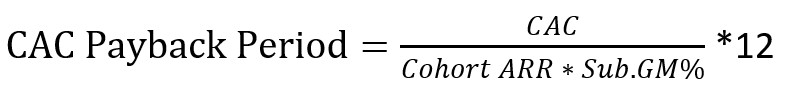
Let’s break down the inputs for the formula.
CAC Payback Period Inputs
There are only three inputs required for this formula which makes it an easy calculation and easily understood. However,
CAC = average customer acquisition cost
Cohort ARR = this is the average ACV of the ARR that we are landing from new customers. It’s not the ARPA of our entire customer base.
Subscription GM % = the margin percentage on just our subscription revenue line
Step 1 – Calculate the CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost)
If you have not calculated CAC previously, I explain how to calculate CAC here. We need our fully loaded Sales and Marketing costs from our SaaS P&L. But we must allocate S&M expenses between new and existing allocation.
Don’t overburden your CAC!

Step 2 – Calculate the CAC Payback Period
To calculate the payback period, you need:
CAC, Cohort ARR, and our subscription gross profit percentage.
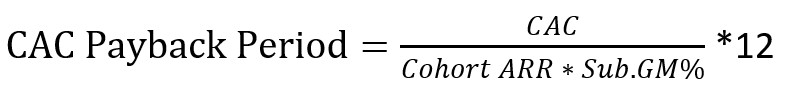
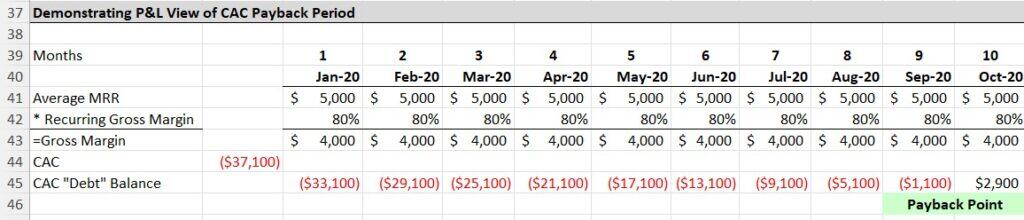
The picture below represents how each month we pay back a portion of our upfront CAC balance. Just like debt.
Important Assumptions
The payback period does not factor in churn or the time value of money. Why is churn important? Think of the payback period like debt repayments as mentioned above. You have a stream of income (MRR – COGS) paying off a portion of the total CAC (i.e. debt) each month. If you lose that stream of income (i.e. customer), you still have to make payments on your debt.
This is the hidden cost of churn. Now, your next customer or customers must pay off their own acquisition costs and the acquisition costs of customers who have churned (assuming you didn’t pay off CAC yet). Even though you might have a nice customer acquisition rate, you are getting deeper into debt with each churned customer.
The more churn you have, the longer it will take your SaaS business to reach a revenue level where you are covering both acquisition costs and the cost to deliver revenue. And remember, you still have other costs to cover (G&A, R&D) below the gross margin level that determine your overall net profitability.
Time Value of Money
Another factor is the time value of money. The formula above does not account for the fact that you are paying off CAC over time. A dollar in the future is worth less than a dollar today.
In my example, the payback period was < 12 months. However, with very long payback periods and cost of capital, your payback period is will increase. This is important for those who have longer payback periods. Not only do you have the “debt” payments, but you also have interest, or opportunity costs, on that money.
CAC Payback Period Benchmarks
What is a good CAC Payback Period? I can answer that, but it also depends. Aggregate SaaS benchmarks are dangerous to your SaaS health. Same is true for CAC Payback Period benchmarks.
You must benchmark your payback period by firmographics. I benchmark by ACV size using Ray Rike’s data at Benchmarkit.ai.
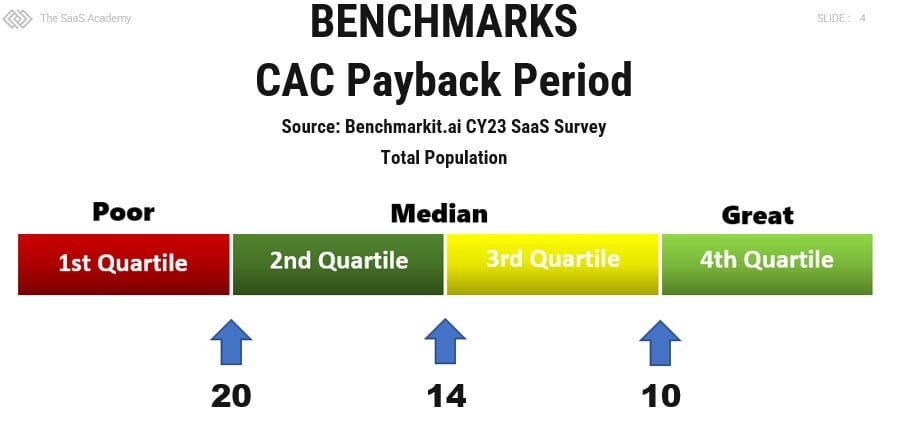
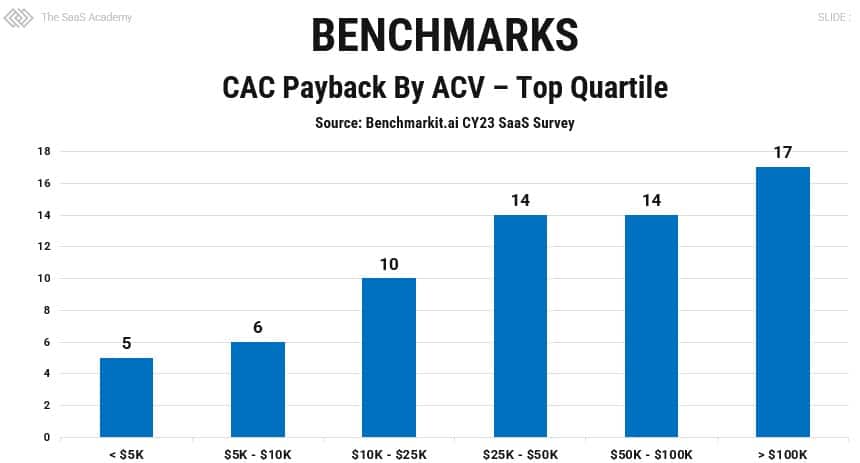
The benchmarks are above are interesting, but I benchmark my SaaS clients by ACV. See below.
CAC Payback Period and Debt
Debt takes on many forms within a company. It could be a bond or a traditional long-term bank loan. Typically, there is a principal balance that you repay over time along with some type of interest component. In this post, I detail how I calculate the CAC Payback Period and how to understand its impact on your SaaS business.
What if I were to say that Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC) were just another form of corporate debt with a twist? You have a balance or principal amount, the amount spent to acquire a new customer, and an interest component. In this case, the interest is the opportunity cost of monies tied up in CAC that could have been spent elsewhere (for example, new product).

Summary
CAC Payback Period is a top operator and investor metric. As traditional debt can steal away our free cash flow, so can your CAC debt. With a few key inputs, you’ll better understand the long-term economics of your SaaS business.
Please enter your valid email below (no spam) for the instant download.
If you do not receive the download, please contact me.
Originally posted January 17th, 2017. Updated March 25, 2025.
I have worked in finance and accounting for 25+ years. I’ve been a SaaS CFO for 9+ years and began my career in the FP&A function. I hold an active Tennessee CPA license and earned my undergraduate degree from the University of Colorado at Boulder and MBA from the University of Iowa. I offer coaching, fractional CFO services, and SaaS finance courses.

[…] are your margins not increasing as expected. Have you calculated your CAC or CAC Payback Period or your Average Cost of Service? If these metrics are out of alignment, your margins could be […]